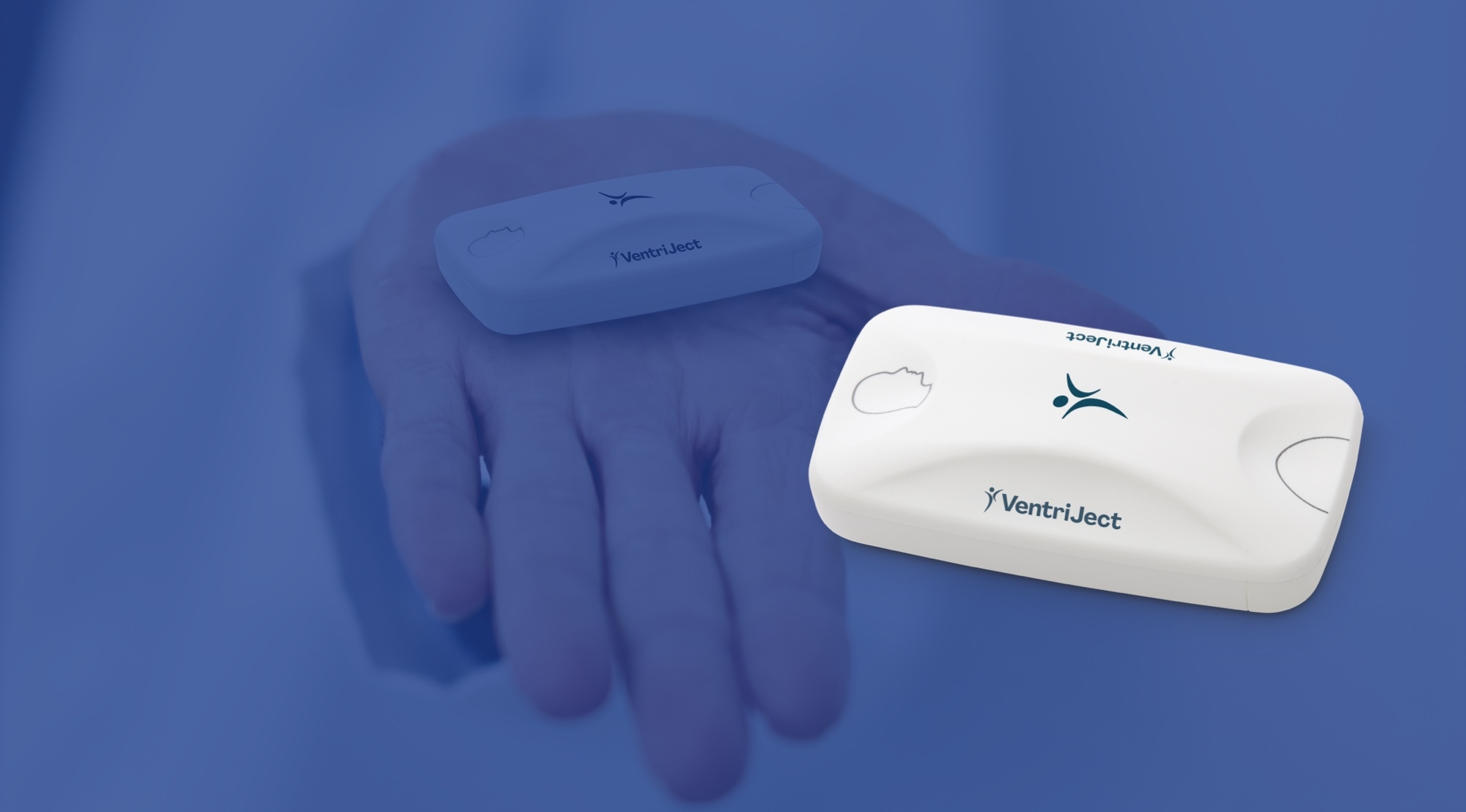
Revolutionizing
VO₂max estimation
Precise estimation of VO₂max in less than 3 minutes with high accuracy and user-friendly simplicity – no exercise required.
Accurate VO₂max estimation in less than 3
minutes from start to finish
 Cardiorespiratory fitness (CRF), measured through VO₂max, can be assessed effortlessly with the award-winning Seismofit® System. The Seismofit® Sensor utilises advanced seismocardiography to capture and analyse the mechanical vibrations generated by the beating heart and transmitted to the chest wall. With the help of a state-of-the-art AI algorithm, a precise VO₂max estimation is delivered in less than 3 minutes, providing quick and reliable results.
Cardiorespiratory fitness (CRF), measured through VO₂max, can be assessed effortlessly with the award-winning Seismofit® System. The Seismofit® Sensor utilises advanced seismocardiography to capture and analyse the mechanical vibrations generated by the beating heart and transmitted to the chest wall. With the help of a state-of-the-art AI algorithm, a precise VO₂max estimation is delivered in less than 3 minutes, providing quick and reliable results.
VO₂max: The ultimate indicator of overall health
VO₂max is considered the paramount indicator of overall health, according to the American Heart Association. It not only measures physical capacity but also serves as a reliable predictor of health outcomes, linking a low VO₂max to an increased risk of premature mortality and various health conditions. Conversely, a high VO₂max can significantly lower mortality risk, potentially by up to 70%, and can reduce the risk of seemingly unrelated diseases, such as prostate cancer, with even a modest 3% increase lowering the risk by 35%.
Source: Importance of assessing cardiorespiratory fitness in clinical practice: a case for fitness as a clinical vital sign: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association.” Circulation 134.24 (2016): e653-e699.
The Heart of Seismofit®: Our Advanced VO₂max Estimation Algorithm
The core of Seismofit®’s technology lies in its advanced VO₂max estimation algorithm, which is central to our patented system. This algorithm is designed to interpret the data captured by the seismocardiography sensor with high accuracy.
Once the seismocardiogram data is transmitted to our secure servers, the algorithm begins a detailed analysis. It processes the raw data by first filtering out noise, ensuring only the most accurate information is considered. The algorithm then examines the average characteristics of multiple heartbeats captured in the seismocardiogram.
Additionally, the algorithm incorporates baseline data such as height, weight, and sex entered by the user into the app. These parameters are crucial as they allow the algorithm to personalise the VO₂max estimation, making it more accurate for each individual. By combining the physiological data with the seismocardiogram, the algorithm can provide a tailored and precise VO₂max estimate.
The analysis involves segmenting the seismocardiogram into individual heartbeats and calculating a mean beat, which serves as a representative sample. Various features are extracted from this mean beat, including the amplitude and frequency of the heart’s vibrations. These features, along with the user’s physiological data, are used by the VO₂max estimation algorithm to deliver an accurate measure of cardiovascular fitness. This comprehensive and personalised approach ensures that Seismofit® provides reliable and actionable VO₂max estimates, enabling users to make informed decisions about their health and fitness regimes. By integrating advanced technology with scientific validation, Seismofit® offers a new approach to cardiovascular fitness assessment.
Validation Studies
Seismofit®’s innovative approach to VO₂max measurement represents a remarkable advancement in cardiorespiratory fitness assessment. While such a capability might seem extraordinary, extensive scientific validation confirms its accuracy. Multiple independent research teams have documented strong correlations between Seismofit's® patented technology and gold-standard laboratory assessments through peer-reviewed studies in respected journals such as Cardiovascular Digital Health Journal and International Journal of Sports Medicine. Here are just three key publications from the growing body of research validating this technology:
- Hernandez, J., et al. (2023). Validity and reliability of seismocardiography for the estimation of cardiorespiratory fitness. Cardiovascular Digital Health Journal, 4(5), 155-163.
- Jensen, M.T., et al. (2023). Accuracy of a Clinical Applicable Method for Prediction of VO₂max Using Seismocardiography. International Journal of Sports Medicine, 44(09), 650-656.
- Martinez, R., et al. (2022). A Chest-Mounted Accelerometer for Estimation of Cardiorespiratory Fitness. Cardiovascular Digital Health Journal, 3(4), 204- 210.